Configuring GNSS and Location Reports
RX Series routers are equipped with location tracking, enabling you to track the movements of a vehicle or other devices that move. The router relays the information of its location as well as other data for use with tracking applications.
Common uses for location reporting include:
- Driver navigation: The router provides real-time location data via the serial or Ethernet port to a local application, including applications that provide mapping and navigation support.
- Computer-Aided Dispatch/Automatic Vehicle Location (CAD/AVL): The router provides real-time location data to the server that tracks the location and other variables of the vehicle or asset.
 Initializing Table Of Contents...
Initializing Table Of Contents...Supported Location Report Protocols
National Marine Electronics Association (NMEA®): NMEA is an ASCII protocol used by many location tracking applications.
Trimble® ASCII Interface Protocol (TAIP): TAIP is a digital communication interface based on printable ASCII characters over a serial data link. TAIP was designed specifically for vehicle tracking applications but has become common in a number of other applications, such as data terminals and portable computers, because of its ease of use.
Hardware Requirements
Ensure that a GNSS antenna is connected to the router. See the RX55 Hardware Guide for installation and antenna connection instructions. For compatible antennas sold by Sierra Wireless, see our website.
After starting up the router, check the GNSS LED to confirm GNSS operation. The GNSS LED will be red while searching for a fix. After getting a fix, it is yellow (Dead Reckoning is enabled but not calibrated) or green (Dead Reckoning is calibrated or disabled). Dead Reckoning enhances vehicle tracking when satellite GNSS service is impeded or unreliable.
See this page for full LED information.
GNSS is the evolution of GPS. GPS uses only a single constellation of satellites, while GNSS uses signalling from up to 4 constellations to provide a more reliable and accurate location fix.
Enabling Location
Under Services > Location > General, ensure that GNSS ENABLE is On.

GNSS is enabled by default, and begins working when the router is powered on with a GNSS antenna connected. GNSS status is reported under GNSS STATE, and can include the following status messages:
- Starting
- Device Unavailable
- Waiting For New Fix
- Location Fix Acquired
For fine tuning GNSS, you can configure the settings listed below:
| SETTING | DESCRIPTION | RANGE | DEFAULT |
|---|---|---|---|
| GNSS ANTENNA BIAS | Optimize the router for the type of connected GNSS antenna |
On (required for active GNSS antenna) Off (compatible only for passive GNSS antenna) |
On |
Configuring Location Reports
Under Location > Reporting:
- Enter the TAIP ID (used for TAIP reports; not required for NMEA). This can be any four-character alphanumeric string as per the TAIP standard.
- Select the NMEA DEVICE ID (PROPRIETARY SENTENCE) (used for NMEA reports; not required for TAIP). Allows use of the router Serial Number or Custom ID (1 to 50 characters) in local IP NMEA reports to identify a device/vehicle. Including the device ID is especially useful when your devices have dynamic IP addresses.
- After selecting Custom ID, you must enter the ID in the CUSTOM ID field.

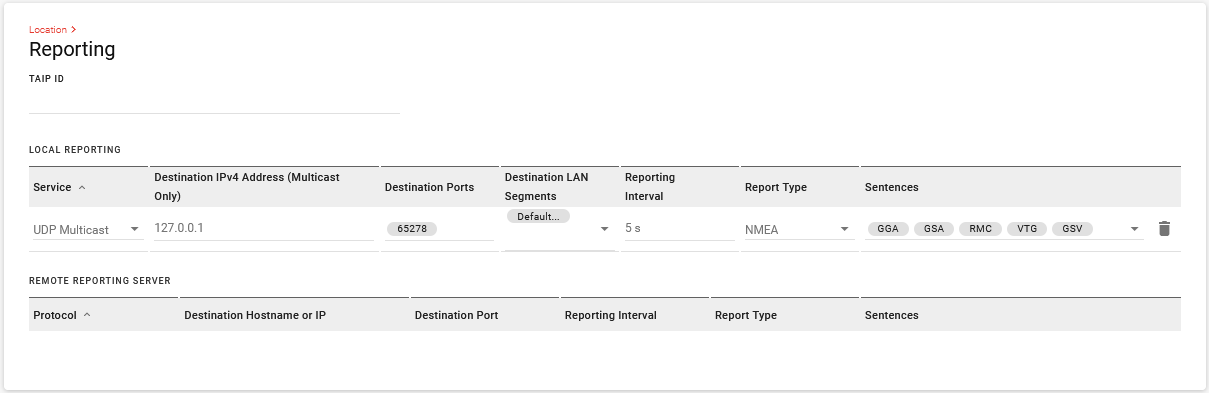
Local Reporting

Local reports are sent via UDP to an IP address on the LAN. For Local Reporting, configure the following:
- Service: UDP Broadcast or UDP Multicast. UDP Multicast needs a Destination IPv4 address.
- Destination IPv4 Address (Multicast Only): To send the location report(s) to a local LAN client, enter the address here. If there is more than one local client, it is advisable to set up a DHCP reservation or set a static IP address on the client.
- Destination Ports: Enter the port on which the CAD/AVL application is configured to receive data (65278 is the default). The port should be available from your CAD/AVL administrator or application documentation.
- Destination LAN Segments: Enter the LAN bridges (network segments) for multiple clients. If you have multiple clients that require the location reports, you can send reports to each client on a particular LAN bridge (network segment).
- Reporting Interval: Sets how frequently (in seconds; 5 seconds by default) the location report is sent to the LAN or IPv4 destination.
Report Type: Select the report type (or protocol, as described above).
- NMEA
- TAIP PV report: TAIP location report that contains PV (Position/Velocity Solution) messages
- TAIP CP report: TAIP location report that contains CP (Compact Position Solution) messages
- TAIP LN report: TAIP location report that contains a long navigation message
- TAIP TM report: TAIP location report that contains the time and date
Sentences: If the report type is NMEA, you can select the desired combination of GGA, GSA, RMC, VTG, and GSV sentences. Some typical sentences are below.
- GGA+VTG: NMEA location report that contains fix information, vector track, and speed over ground
- GGA+VTG+RMC: NMEA location report that contains fix information, vector track, speed over ground, and recommended minimum location data
- GGA+VTG+RMC+GSA+GSV: NMEA location report that contains fix information, vector track, speed over ground, the recommended minimum location data, overall satellite data, and detailed satellite data
Remote Reporting

For Remote Reporting, configure the following REMOTE REPORTING SERVER settings, as applicable:
- Protocol: TCP or UDP
- Destination Hostname or IP - IP address or FQDN (fully qualified domain name) of the server where location reports are sent. Example: 192.100.100.100. The IP address can be for a local host or a remote server that is accessed over-the-air or via a VPN tunnel. If an IP with the last octet of 255 is configured (i.e. 192.168.13.255), a report would be broadcast to all IPs on that subnet. When configured to a local host subnet, any connected device would receive the report. Note: If you want to use it as a LAN device, it must have a private IP address. If you want to use a public IP address, use a Local IP report.
- Destination Port: Destination port on the server where location reports are sent. The destination port can be the same for all servers or you can configure a different destination port for each server. Range: 1–65535 (default for the first server is 22335).
- Reporting Interval: - Sets how frequently (in seconds; 5 seconds by default) the location report is sent to the IPv4 destination
- Report Type: Select the report type (or protocol, as described above).
- NMEA
- TAIP PV report: TAIP location report that contains position and velocity
- TAIP CP report: TAIP location report that contains the compact position
- TAIP LN report: TAIP location report that contains a long navigation message
- TAIP TM report: TAIP location report that contains the time and date
- Sentences: For NMEA reports, you can select the desired combination of GGA, GSA, RMC, VTG, and GSV sentences. Some typical sentences are below.
- GGA+VTG: NMEA location report that contains fix information, vector track, and speed over ground
- GGA+VTG+RMC: NMEA location report that contains fix information, vector track, speed over ground, and recommended minimum location data
- GGA+VTG+RMC+GSA+GSV: NMEA location report that contains fix information, vector track, speed over ground, the recommended minimum location data, overall satellite data, and detailed satellite data
Forwarding Local Reports to the Serial Port
It is possible to send reports via the RJ45 Serial port on the router using the loopback address (127.0.0.1) and then setting the Serial port in PAD mode to listen and forward to the serial port. This configuration is useful in cases where local serial forwarding is used for sending reports to laptops in docking stations in a service vehicle.
To configure sending local reports to the Serial Port:
Under Location > Reporting > LOCAL REPORTING, configure Local Reporting for UDP Multicast using the loopback address (127.0.0.1).
Go to Hardware Interfaces.
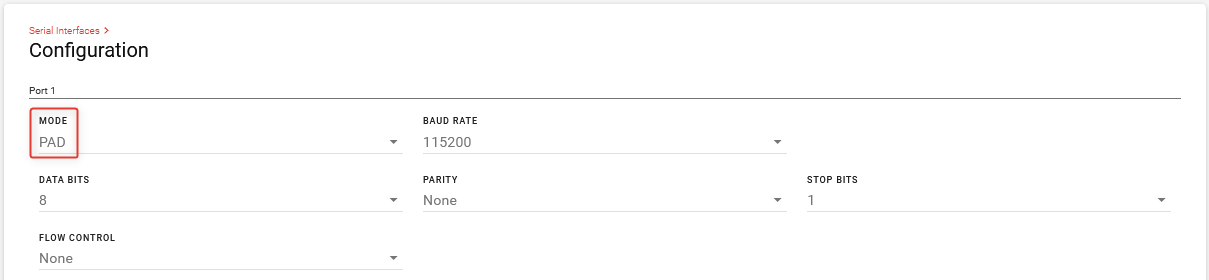
Under Serial Interfaces > Configuration, set the MODE for Port 1 to PAD.
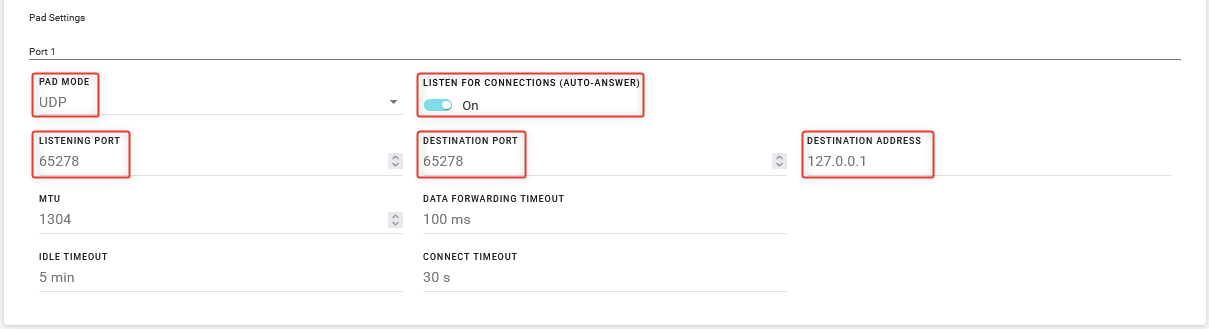
Under PAD Settings, configure Port 1 as follows:
- PAD MODE: UDP
- LISTEN FOR CONNECTIONS (AUTO-ANSWER): On
- LISTENING PORT and DESTINATION PORT: Same port configured in Step 1
- DESTINATION ADDRESS: Same Destination IP Address used in Step 1 (127.0.0.1)
The receiving application may have additional requirements for reducing the BAUD rate or configuring other flow control parameters. Consult the documentation from the application vendor for details.
Click SAVE.
To confirm operation, open the CAD/AVL listening application on your computer and confirm that messages are being received and understood.
Sending GPIO State Information
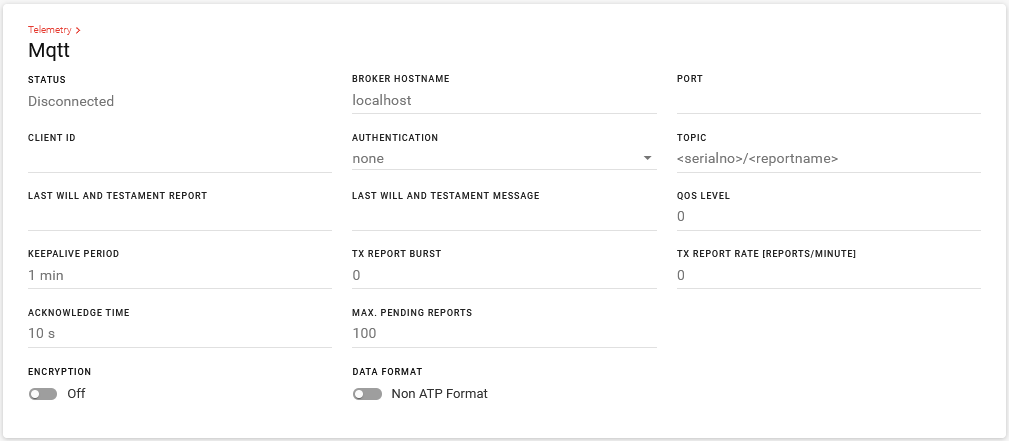
You can send GPIO status along with device location to an MQTT server using the Telemetry reporting feature.

The Report Title General Purpose Inputs exists by default, and is reported at each GPIO state change by default. This report sends the report GPIO ARA, which consists of the following data points:
- atp.glon: GPS Longitude (decimal degrees)
- atp.glat: GPS Latitude (decimal degrees)
- atp.ghed: GPS Heading (decimal degrees)
- atp.gpi: GPIOCumulativeBits, which is a binary report of the GPIO data point for the Primary GPIO Input (on power connector) 0th bit: atp.pgpio
To send GPIO and location information to an MQTT server:
Go to Telemetry > General, turn on SERVICE.

Go to Telemetry > Reporting, under REPORT MODE, select one of the MQTT options: MQTT or AirVantage and MQTT.
Under Telemetry > MQTT, configure the connection to your MQTT server.