MQTT security
 Initializing Table Of Contents...
Initializing Table Of Contents...Security Modes
This page explains how to secure your communication to AirVantage when using MQTT. Three methods are supported:
- MQTT with user/password: Authentication with MQTT user/password, no encryption and no server authentication (not to be used in production). Port: 1883
- MQTT/TLS (one-way authentication): Secure channel over TLS 1.2 (Server authentication and encryption) based on user/password to authenticate the device, and the AirVantage’s certificate to authenticate the server. Port: 8883
- MQTT/TLS (mutual authentication): Mutual certificate-based authentication (server and device) & encryption. Port: 8883
When the mutual authentication with certificates is used, the user/password authentication mechanism will not be taken into account here.
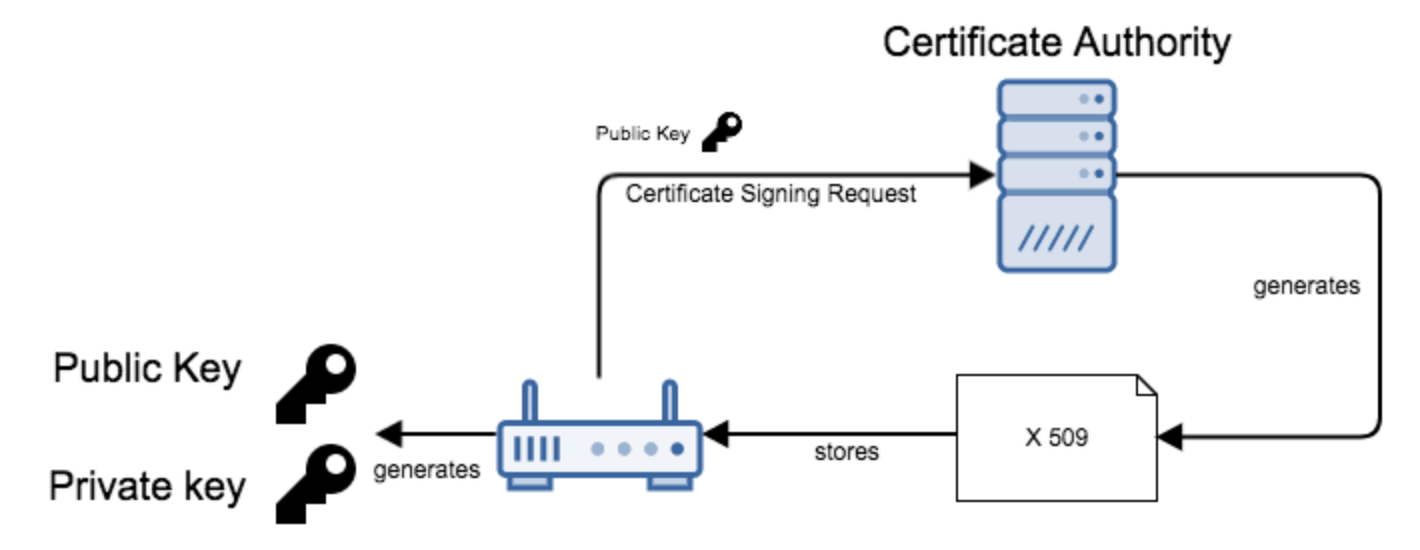
Key generation
Certificates are issued based on authentication of public keys, and must be signed by a Certification Authority (CA).
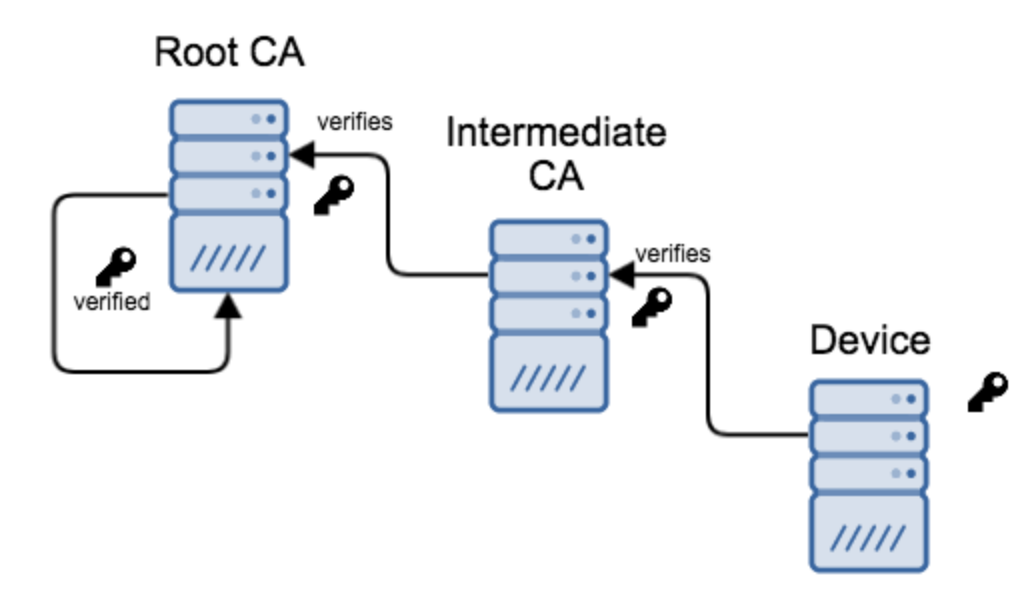
About Certificates validation chain & revocation...
A certificate can be signed by an intermediate CA, which can be itself signed by another intermediate CA - and so forth, until a trusted root CA is reached.
By following the CA chain, the identity and validity of a certificate owner can be verified and trusted.
AirVantage manages the certificate revocation.
Username/Password Configuration
In order to configure the device’s “username” and password in AirVantage, follow the tutorial below:
- Define the contract between your device and AirVantage using the How to write an application with AirVantage .
- When your application has been deployed in AirVantage, associate it to your device and set the password to Connect your device to AirVantage .
In this case, the application model must include this security parameter:
<protocol comm-id="SERIAL" type="MQTT" >
<parameter name="mqtt-security" value="user-password"/>
</protocol>
TLS Configuration
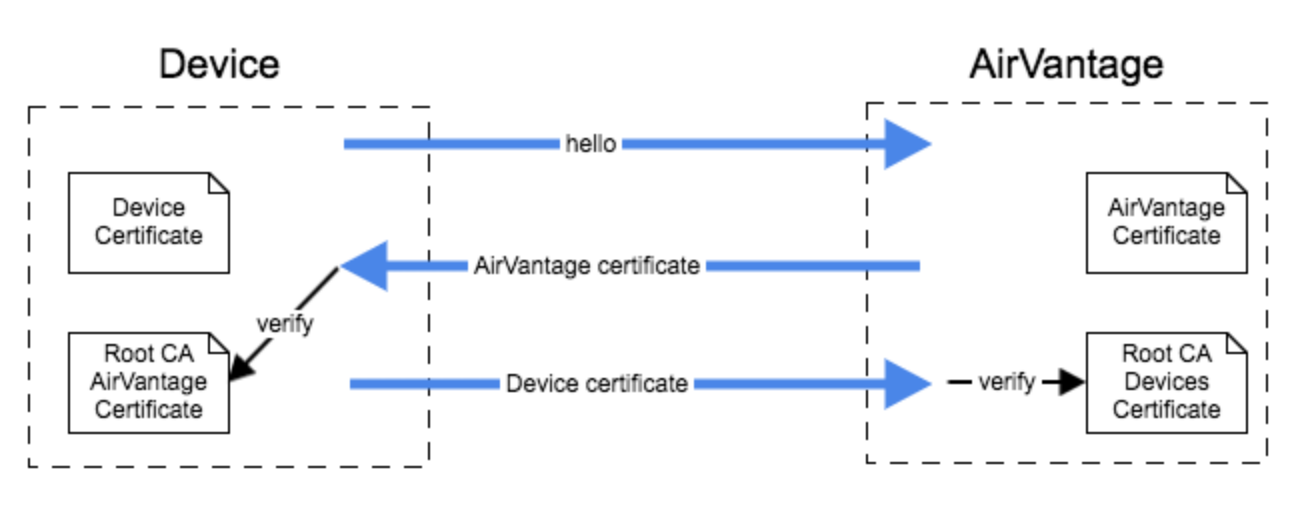
AirVantage Certificate
The AirVantage root CA is goDaddy. Get the AirVantage root CA certificate . The AirVantage CA ROOT certificate has to be stored in the hardware memory in order to validate AirVantage identity.
Device Certificate
Upload your root CA certificate to AirVantage (Contact the support team to upload this certificate).
Your certificate must include the following requirements:
- Certificate Common Name (CN) has to be the « communication ID », that is to say the IMEI or any Serial Number (according to what has been configured in the application model ).
- The hardware certificate has really been signed by customer’s PKI, using customer’s CA root certificate configured in the customer’s company,
- The MQTT topic path where the data will be pushed, really corresponds to the communication ID (IMEI, Serial number, …) declared in the certificate CN.
<protocol comm-id="SERIAL" type="MQTT" >
<parameter name="mqtt-security" value="x509"/>
</protocol>
Supported Cipher suites
AirVantage supports TLS 1.2 and the following cipher suites:
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA,
TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA,
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA,
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA,
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA,
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA,
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,
TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
An AirVantage public key is signed with a RSA key. As a consequence a cipher suite based on this mechanism has to be selected.
More…
Data integrity can be guaranteed by the embedded application by adding a signature of the data in each JSON message. This signature must be in the DATA section of the JSON format. Thus the signature will be taken as an additional datapoint of the solution.
Example:
{"14037939309874": {
"dongle.serial": "11111111111",
"vehicle.tire.pressure": "2.2",
"signature" : "AADDFE3245"}
}
Example
AirVantage expects the MQTT client to :
- have access to a certificate from its Root CA
- connect to a MQTTS endpoint (eg “mqtts://eu.airvantage.net:8883”) corresponding to its Root CA
- send its TLS certificate (option “tls.RequireAndVerifyClientCert” will be set on the server side)
- use its “MQTT Comm Id” as the “CommonName” field
- set the “server_name” TLS extension properly
Here’s an example of a SWIR client connecting using a certificate issued by ClientCA”:
var mqtt = require('mqtt');
var fs = require("fs");
var rootCA = fs.readFileSync("~/secu/SSLCA/root/rootca.crt");
var clientCert = fs.readFileSync("~/secu/client.crt");
var clientKey = fs.readFileSync("~/secu/client.key");
var client = mqtt.connect('mqtts://eu.airvantage.net:8883', {
ca : [rootCA],
cert : clientCert,
key : clientKey,
servername : "mqtt.eu.airvantage.net"
});
And here’s the corresponding client connecting with a certificate issued by the customer’s CA:
#!/usr/bin/env node
var mqtt = require('mqtt');
var fs = require("fs");
var rootCA = fs.readFileSync("~/secu/SSLCA/root2/rootca2.crt");
var clientCert = fs.readFileSync("~/secu/customer-client.crt");
var clientKey = fs.readFileSync("~/secu/customer-client.key");
// Note that the client is using the customer's URL
var client = mqtt.connect('mqtts://eu.airvantage.net:8883', {
ca : [rootCA],
cert : clientCert,
key : clientKey,
servername : "customer.eu.airvantage.net"
});