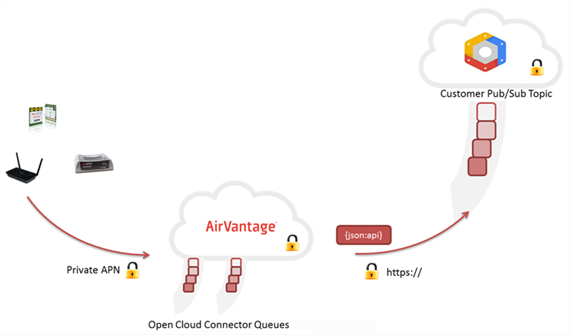
Cloud Connectors
This document describes the available connectors:
- HTTP Callback (Webhook) mechanism if the connection is initiated from an alert rule.
- Google Pub Sub Connector if your application is hosted on Google Cloud
- AWS Kinesis Stream/Firehose Connector if your application is hosted on Amazon Web Services.
- Micorsoft Azure EventHub Connector if your application is hosted on Microsoft Azure.
- AMQP Connector if you have an application to open the stream and handle a high level of messages
 Initializing Table Of Contents...
Initializing Table Of Contents...HTTP Callback
Many public APIs use callbacks to notify API consumers of specific events. For example, if you configure the callback url when creating an alert rule, an HTTP request will be sent to a specified URL when the alert is raised.
This is a stateless procedure and messages are sent in JSON format with the content-type “application/json”. Messages sent to an unreachable endpoint will be lost.
To receive messages throughout HTTP callbacks, you can contact our support team or use the APIs likely to raise events.
Google Pub/Sub Connector
The Google Pub sub mechanism is a publish-subscribe connector for applications hosted on the Google Cloud Platform.
AirVantage publishes the new operations status, the alerts and the new raw data in your topic using the fully-documented JSON format below. No password is stored on Sierra Wireless’ side: AirVantage uses IAM authentication. Messages are sent using https. Optimized to handle a high volume of messages (retry mechanism, bulk send). You can easily operate and scale your application. You maintain control over your topic: you can stop or unauthorize Sierra Wireless’s access to your topic at any time using Google Cloud Platform, as explained here .
Configuration
Have a look to the Google Howto for a full description about how to configure this connector.
AWS Kinesis Connector
The AWS Kinesis mechanism is a publish-subscribe connector for applications hosted on the Amazon Web Services Cloud.
AirVantage publishes the new operations status, the alerts and the new raw data in your stream using the fully-documented JSON format below. No password is stored on Sierra Wireless’ side: AirVantage uses IAM authentication.
Messages are sent using https. Optimized to handle a high volume of messages (retry mechanism, bulk send). You can easily operate and scale your application. You maintain control over your topic: you can stop or unauthorize Sierra Wireless’s access to your topic at any time using AWS.
This connector uses a random partition key to evenly spread the load across destination shards.
Why to use Kinesis connector?
Kinesis supplies several great features if you have a huge amount of data to send but on the other hand, it can be complex to implement. Here some tips to help you to make your choice. Select kinesis if:
- High Pace of data: you have a high pace of messages to receive and to process (counting, aggregating and filtering) on the fly as a FIFO. You can have multiple producers and multiple consumers, each one can process the same data for its own use: storing, dashbording, … Each application can re read the messages within 24 hours.
- Data processing: you want to process your data or a subset of data to generate analytics. Kinesis allows you to store your data on a single machine according to a criteria to filter them: these data will be fully available and your processing will be more efficient.
- Acknowledgement: Your application will acknowledge a set of messages. If no acknowledgement has been done, all the messages from the previous acknowledgement will be sent again, your application may received some messages twice and so deal with them.
Using Firehose connector, you can send event to some third party tool like QLikview, Splunk, …
Configuration
Go to the Kinesis Howto for a full description about how to configure the Kinesis Stream connector.
Go to the Firehose Howto for a full description about how to configure the Kinesis Firehose connector.
Resources
- We supply tutorial to help you to configure and use these connectors here
- Have a look to this getting started to start with Kinesis.
- This connector supplied by AWS will help you to consume your data easily and store it (for example in S3 data storage). You may want to use Amazon Firehose as well.
Microsoft Azure EventHub Connector
The Mircosoft Azure EventHub stream is a producer-consumer connector for applications hosted on the Microsoft Azure Services Cloud.
AirVantage publishes the new operations status, the alerts and the new raw data in your stream using the fully-documented JSON format
. No password is stored on Sierra Wireless’ side: AirVantage uses a connection string you have to generate in the Microsoft Azure Console in order to give access to AirVantage.
Messages are sent using https. Optimized to handle a high volume of messages (retry mechanism, bulk send), you can easily operate and scale your application, you maintain control over your stream: you can stop or unauthorize Sierra Wireless’s access to your topic at any time using the Microsoft Azure Administration console.
EventHub is limited to event lesser than 256k (see this page , section
Batch event send operations). So you may avoid to push over-sized data.Other limitations can be applied according to the selected offer (see Event Hubs Pricing page).
Configuration
Have a look to the Azure EventHub Howto for a full description about how to configure this connector.
Resources
- Have a look to this tutorial to start with EventHub
- Getting started with AirVantage & Azure EventHub
AMQP Connector
The Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) is an open standard for passing messages between applications. Visit official AMQP site for further information. Currently the version 0.9.1 of the protocol is used.
To connect to the broker you will need some configuration elements in your remote system:
- the host name or IP address of the AMQP broker
- the connection port. Default value is 5672.
- the virtual host, will isolate “environments” (groups of users, exchanges, queues and so on) to ensure that messages are only visible by the right partner.
- the user name
- the password
- the queue name
- the list of data path you want to be sent on this queue: empty if no filtering mechanism or a coma-separated list like
car1.engine.sparkplug.state, car1.engine.speedto specify the data (contact your support team if you want to activate this option).
AirVantage can provide an AMQP broker for our partners to consume event messages from our server. Configuration elements are provided by Sierra Wireless. Please contact our support team.
Permissions will be set to “basic.get” and “basic.consume” only.
Once your connection established to your AMQP broker, it will remain alive. All messages put into the queue will be available for a week. After this period the messages will expire if they are not consumed.
The standard operating mode of AMQP message consumption is a “Push” mode. Once the remote system is connected to the broker and bound to a queue, any new message will be received automatically.
During the message consumption by a remote service, the message needs to be acknowledged. Each time a message is acknowledged, it will be removed definitively from the queue. If a message is consumed but not acknowledged, it will be put back in the queue and then available again.
Tip: avoid using the client API “auto acknowledgment” system.
See the sample code with a tutorial and read it carefully to know all the best practices.