Configuring Port Forwarding
Port Forwarding rules are used to direct incoming WAN traffic on single ports or range of ports (e.g., from remote servers and devices) to corresponding ports on specific devices on your LAN.
By default, AirLink OS blocks all incoming unsolicited traffic (packets). However, any unsolicited traffic that is captured by a port forwarding rule is forwarded to the rule’s specified LAN device.
To configure a port forwarding rule:
Go to Networking > Firewall > Port Forwarding Rules.
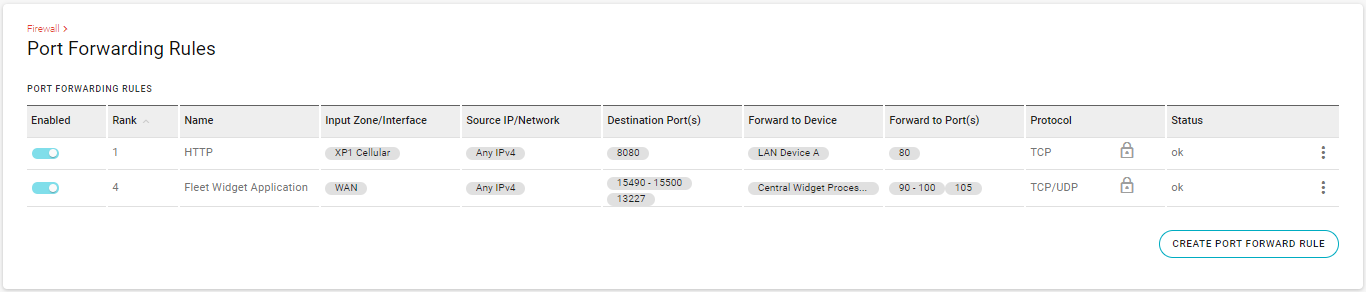
Click CREATE PORT FORWARD RULE to create a new rule, or click Edit at the end of a row to update an existing rule.
Begin configuring the Port Forwarding Rule.
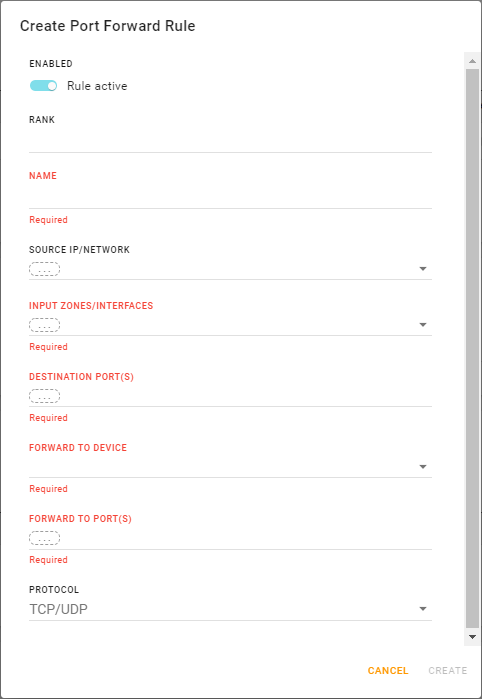
If you want the rule to be used as soon as it is saved, ensure ENABLED is selected to activate the rule.
Enter the rule’s RANK. Port forwarding rules are applied to incoming traffic by their rank order — the rule with the lowest rank (minimum 1) is applied first.
Note — Do not enter a rank ≤ 0. The rank change will not be accepted and the original value stays.Enter a unique NAME to identify the rule when it appears in the PORT FORWARDING RULES table.
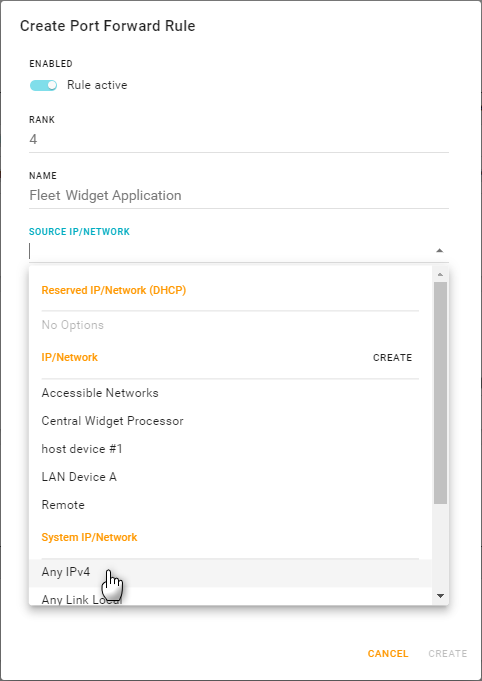
Optionally, select specific incoming traffic sources (IPs or networks) on which the rule will be applied. Click the SOURCE IP/NETWORK field and then add as many sources as you want.
Tip To limit access to specific devices, create and use a source IP/Network with an appropriate source IP address range. For example, to allow access only to the devices on a private APN network, a source address range like 10.10.0.0/24 could be used.)
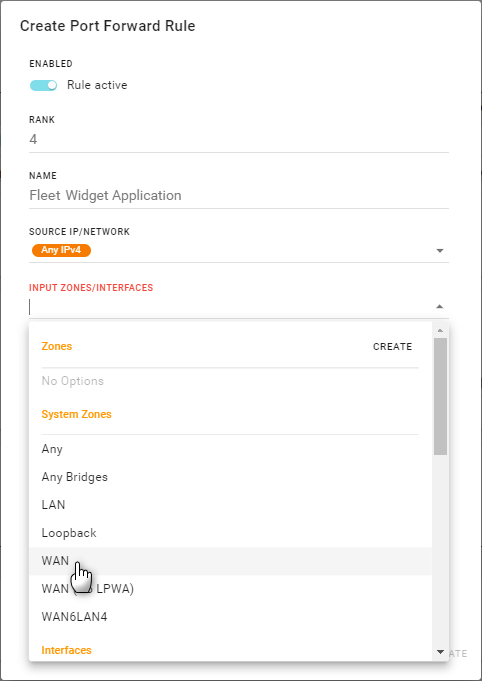
Click the INPUT ZONES/INTERFACES field to select the specific incoming traffic Zones (System Zones or your own defined zones) or interfaces on which the rule will be applied. Add as many zones and interfaces as you want. (Note that port forwarding is typically performed on incoming WAN traffic, but LAN-to-LAN port forwarding is also supported, if needed.)
Tip If only specific interfaces require forwarding, use narrowly-focused zones instead of all-encompassing zones. For example, if the WAN zone is selected, port forwarding is performed for all WAN devices. However, if only two specific WAN interfaces need to be forwarded, create and use a zone containing only those specific interfaces.
Enter the incoming traffic’s intended DESTINATION PORT(S) (single ports or ranges) that are to be redirected (forwarded) by the rule.
Click the FORWARD TO DEVICE field to select the destination device (Reserved Device (DHCP), or Device) that will receive all the incoming traffic forwarded by the rule.
You may want to select a Reserved Device (DHCP) to ensure that your selected device’s IP address does not change. You can create a DHCP reservation at Networking > DCHP Reservation.
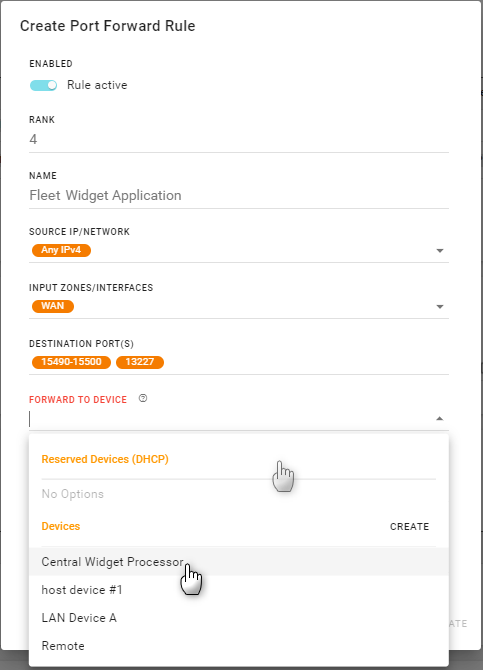
Enter the destination device’s FORWARD TO PORT(S) (single ports or ranges) that will receive the forwarded traffic.
Note — The “Destination Ports” must map 1:1 with the “Forward To Ports”.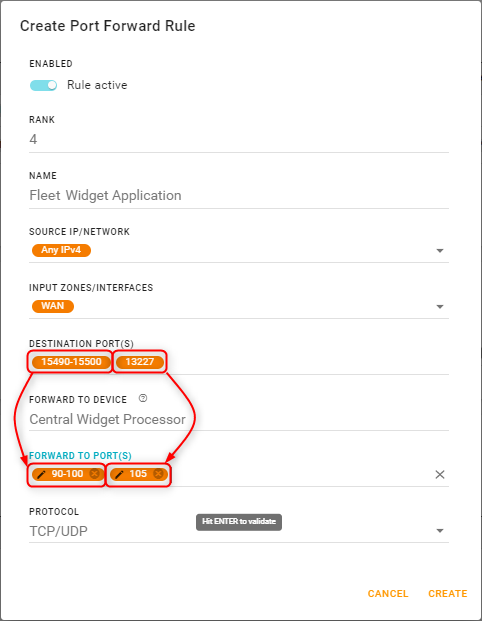
For example, in the rule shown above, DESTINATION PORT(S) = 15490-15500, 13227 and FORWARD TO PORT(S) = 90-100, 105.
AirLink OS maps 15490-15500→90-100, and 13227→105.Click the PROTOCOL field to select which traffic type(s) will be forwarded.
- TCP/UDP — All traffic is forwarded.
- TCP — Only TCP traffic is forwarded.
- UDP — Only UDP traffic is forwarded.
Click CREATE or UPDATE to save the rule.
AirLink OS validates the rule and updates the Status field in PORT FORWARDING RULES table with “ok” or an error message (e.g., “Invalid DNAT Source Address, forwarding between Ipv4 and Ipv6 is not supported”, “Invalid DNAT port mapping, port(s) not specified”, etc.)
For example, the table shown below has two rules. The first rule (status=“ok”) will be used immediately, but the second rule will not be used until the error is fixed — edit the rule to correct the reported problem.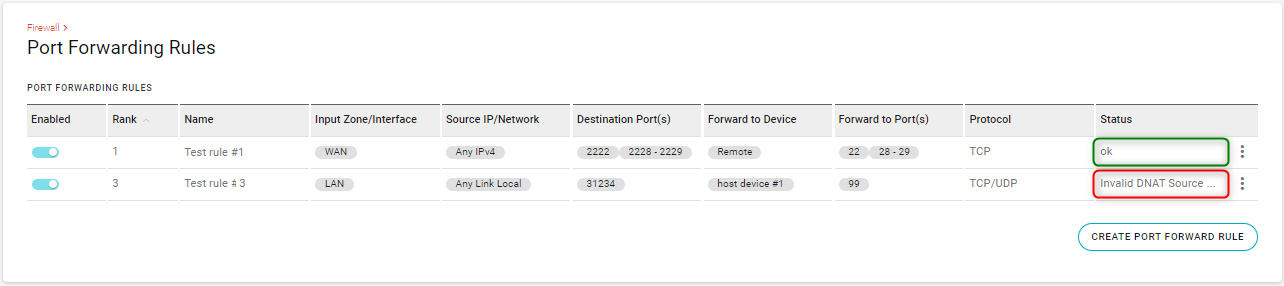
 Searching...
Searching...







